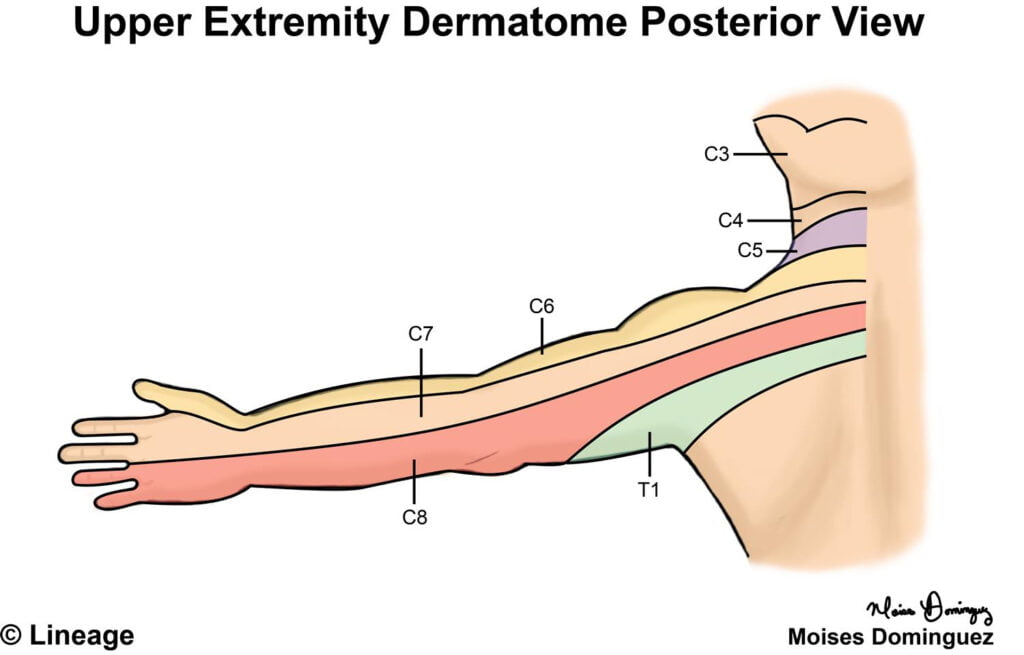
Dermatomes Chart Hand – The term “dermatome” is a combination of 2 Ancient Greek words; “derma” meaning “skin”, and “tome”, meaning “cutting” or “thin section”. It is a location of skin which is innervated by the posterior (dorsal) root of a single back nerve. As posterior roots are organized in sections, dermatomes are. This is why the term “dermatome” describes the segmental innervation of the skin.
Dermatomes Neurology Medbullets Step 1 – Dermatomes Neurology Medbullets Step 1
Neighboring dermatomes often, if not constantly overlap to some degree with each other, as the sensory peripheral branches representing one posterior root normally exceed the limit of their dermatome. The thin lines seen in the dermatome maps are more of a clinical guide than a real boundary. Dermatomes Chart Hand
This means that if a single spinal nerve is affected, there is most likely still some degree of innervation to that sector of skin originating from above and below. For a dermatome to be entirely numb, normally two or three surrounding posterior roots need to be affected. In addition, it’s important to keep in mind that dermatomes go through a big degree of interindividual variation. A graphical representation of all the dermatomes on a body surface chart is referred to as a dermatome map. Dermatomes Chart Hand
Dermatome maps
Dermatome maps illustrate the sensory circulation of each dermatome across the body. Clinicians can examine cutaneous sensation with a dermatome map as a method to localize lesions within main nervous tissue, injury to particular spinal nerves, and to identify the degree of the injury. Numerous dermatome maps have been developed throughout the years however are typically conflicting.
The most commonly utilized dermatome maps in major books are the Keegan and Garrett map (1948) which leans towards a developmental analysis of this principle, and the Foerster map (1933) which associates better with clinical practice. This article will examine the dermatomes using both maps, identifying and comparing the major differences in between them.
Why Are Dermatomes Important?
To comprehend dermatomes, it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the spinal column. The spine is divided into 31 sectors, each with a pair (right and left) of anterior and posterior nerve roots. The types of nerves in the posterior and anterior roots are various.
Anterior nerve roots are responsible for motor signals to the body, and posterior nerve roots get sensory signals like pain or other sensory symptoms. The anterior and posterior nerve roots combine on each side to form the spine nerves as they leave the vertebral canal (the bones of the spine, or backbone).